Chickenpox in children: early signs, symptoms and treatment
90% of kids will catch chickenpox before they turn 10, so make sure you're clued up about how to manage the itch. We look into the signs, symptoms and treatment of this highly contagious illness and bust some of the myths that surround it. From how long it lasts to whether you can catch it twice, here's what you need to know.
No sooner do you Google the symptoms of chickenpox than you're overwhelmed with a sea of information about it – not all of it true.
With the help of some chickenpox experts, we've gathered the facts and cleared up all those chickenpox myths to bring you the truth about this common childhood disease.
Here are the questions you're just itching (ahem) to know the answers to ...
FREE NEWBORN NAPPIES
What is chickenpox?
The NHS describes chickenpox as a 'common illness that mainly affects children and causes an itchy, spotty rash.'
Caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), it usually causes an itchy red, blister-like rash. Although the spots disappear, the virus stays dormant in your body for the rest of your life. Later in life, the virus can be reactivated (often triggered by age, stress or low immune system) causing shingles.
Experts believe the virus peaks in winter and spring, particularly between March and May.
How is chickenpox spread?
Chickenpox is very contagious. The infection is spread in the fluid found in chickenpox blisters and the droplets in the coughs or sneezes of someone with the infection.
According to the NHS, you can catch chickenpox from:

- contaminated surfaces
- contaminated objects, such as toys or bedding
- touching chickenpox blisters or the shingles rash
- face-to-face contact with an infected person, such as having a conversation
- being in the same room as an infected person for 15 minutes or more.
What are the signs and symptoms of chickenpox?
Chickenpox usually develops in babies and children as follows:
- Mild flu-like symptoms Before any spots appear, your child may have symptoms like a raised temperature, headache, achy muscles, loss of appetite and a general feeling of being unwell. Some parents describe their child as ‘grouchy’, ‘off-colour’ or ‘irritable’.
- Red spots Itchy red spots appear – often in clusters behind the ears, on the face, on the chest and stomach, and on the arms and legs. It's at this point that you may be wondering whether it's definitely chickenpox.
- Spots turn into blisters The red spots fill with fluid – the tell-tale sign of chickenpox.
- Spots scab over Some blisters burst and turn into itchy scabs, while new blisters may still be forming.
How can I tell if my child has chickenpox?
Sharon White, registered nurse, midwife and qualified school nurse says:
'If your child has been in contact with other kids who have it or if it has been going round their nursery or school, then it is likely to be chickenpox as it's highly contagious.'
But you'll soon know for sure as with chickenpox, these first few red spots spread over the body and develop into itchy, fluid-filled blisters in the first 24 hours or so of them appearing.
They can even pop up in the mouth (putting little ones off their food), in their hair, genital area and even along lash lines.
Over the next few days, these blisters will dry out and begin to crust over. Within a week or two, the crusted scab will fall off naturally.
While some children are covered head to toe in spots and blisters, others may only get one or two spots and the illness may even go unnoticed.
What do chickenpox spots and blisters look like?
1. Chickenpox blister
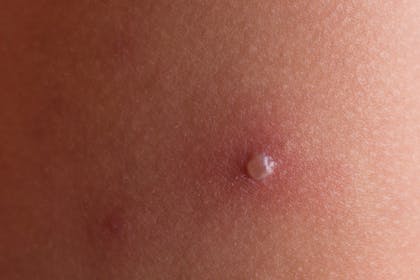
This is how you may first notice chickenpox appear - as red spots or blisters, usually on the face, neck or tummy.
2. Chickenpox rash
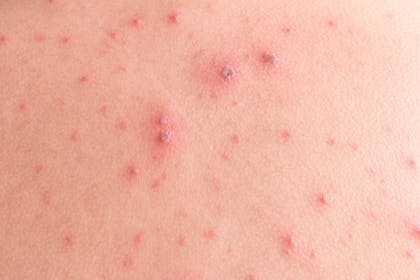
After a day or two, a red rash will appear and spread. It will most likely be a mix of red spots and blisters.
3. Chickenpox blisters crusting over
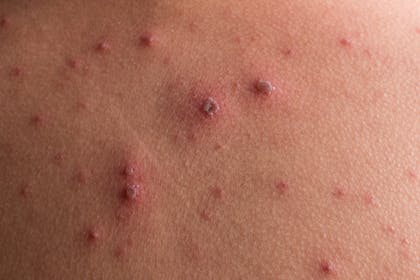
The chickenpox blisters will gradually start to crust over or scab. Make sure little ones don't itch or pick at them as they can scar.
4. Chickenpox scabs
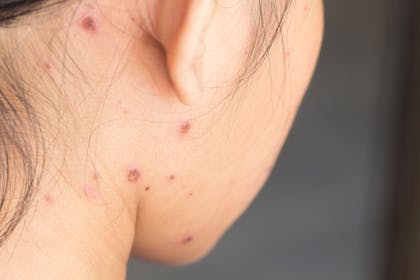
After a week or two, the chickenpox blisters and scabs will gradually fade.
Need advice?
Our health visitors and nursery nurses are online Monday to Friday evenings to answer your queries on feeding, sleep and child health.
How long should children stay off school for with chickenpox?
'Your child will remain contagious until the last pox has crusted over. This normally takes about five or six days after the rash first appeared,' says Sharon.
'You'll need to keep them off nursery or school until all spots have crusted over, which normally takes around seven days.'
Do I need to see the doctor for chickenpox?
There's no need to see your GP if your child has chickenpox. However, if you are concerned, then the best thing to do is to phone up your GP and ask them what to do.
If your child needs to be seen, they may want to keep you away from other patients by asking you to wait in a different room to the waiting room. This is to make sure you don’t pass the infection on to people who are at risk of complications from it, such as women who are pregnant.
How do you treat chickenpox?
'Paracetamol can be used to help alleviate symptoms such as fever and pain,' explains Dr Nasir Hannan, GP at The London General Practice. However, 'Ibuprofen or other anti-inflammatories should not be used in children or adults with chickenpox,' he warns.
'Drink plenty of fluids to avoid dehydration, wear loose comfortable cotton clothing and keep nails short to avoid scratching,' adds Dr Hannan.
Generally your GP will recommend treating it as follows:
- use paracetamol to relieve fever and discomfort – don't use anti-inflammatory painkillers, such as ibuprofen, as they can sometimes make people with chickenpox very ill
- use calamine lotion, moisturising creams or cooling gels to ease itching. (A lot of parents ask, Can I use Sudocrem on chickenpox? We get the answer from a GP!)
- tap or pat the skin rather than scratching it – it's important to avoid scratching because this can lead to further problems, such as infected spots
- drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated.
You should also take steps to stop chickenpox spreading, such as staying away from school or work until the last blister has scabbed over.
NHS advice suggests contacting your GP or NHS 111 if:
- you're not sure if you or your child has chickenpox
- the skin around the blisters is red, hot or painful (signs of infection)
- your child is dehydrated
- your baby is less than four weeks old and has chickenpox
- you develop chickenpox as an adult
- the symptoms haven't started to improve after six days
- you've been in contact with someone who has chickenpox (or you have symptoms) and you're pregnant or have a weakened immune system
- you or your child has signs of chickenpox complications, such as swollen and painful skin, difficulty breathing or dehydration.
Can you get chickenpox twice?
This is an interesting question and one that's often asked in our Coffeehouse Forum. A common misconception among mums is that if your baby catches chickenpox before they reach the age of one, they will catch it again.
There is no actual research to suggest this is true.
Official NHS advice regarding getting chickenpox twice suggests it is extremely rare, stating:
'Once you’ve had chickenpox, you usually develop antibodies to the infection and become immune to catching it again.
'However, some people who have had chickenpox will develop a related condition called shingles later on. This is caused by the chickenpox virus being reactivated, usually several decades later.'
Is there a chickenpox jab?
There is a chickenpox vaccination but it is not part of the current NHS childhood immunisation schedule.
The NHS only offers the vaccine to children and adults who are particularly vulnerable to complications of the illness, such as those with a weakened immune system.
It is also given to those in contact with people at risk, for example the brothers and sisters of a child with leukaemia or a child whose parent is undergoing chemotherapy.
If you want to get your child vaccinated, you can get it done privately. This has to be done over the age of 12 months and is likely to cost around £70 per dose (two doses in a course). It is very safe and is 98% effective in children.
Read our story about why one mum paid £260 to stop her children getting chickepox.
It is available privately at certain Superdrug, Boots and CityDoc among others.
Why aren't children in the UK vaccinated against chickenpox?
Although chickenpox vaccinations are part of the routine immunisation schedule in the United States and Germany, the UK's immunisation body has decided against universal vaccination of children. This is due to the cost as well as fears that it could increase shingles among adults.
This is how the NHS explains the decision:
'If a childhood chickenpox vaccination programme was introduced, people would not catch chickenpox as children because the infection would no longer circulate in areas where the majority of children had been vaccinated.
'This would leave unvaccinated children susceptible to contracting chickenpox as adults, when they are more likely to develop a more severe infection or a secondary complication, or in pregnancy, when there is a risk of the infection harming the baby.
'We could also see a significant increase in cases of shingles in adults. Being exposed to chickenpox as an adult – for example, through contact with infected children – boosts your immunity to shingles.
If you vaccinate children against chickenpox, you lose this natural boosting, so immunity in adults will drop and more shingles cases will occur.'
Sarah Allen, a British mum whose son, Jasper, had an extremely severe case of chickenpox believes that no child should suffer.
She is currently campaigning to make the chickenpox jab available on the NHS.
Is chickenpox harmful in pregnancy?
It is extremely rare to get chickenpox when you're pregnant. In fact, according to the NHS, in the UK only three in every 1,000 women (0.3%) catch chickenpox during pregnancy.
However, it is still a good idea to seek advice from your GP or midwife immediately if you're pregnant and:
- you think you may have chickenpox
- you've never had chickenpox or you're not sure, and you've been near someone who has it (even if you have no rash or other symptoms)
- you get chickenpox within seven days of giving birth.
Find out more about exposure to chickenpox when you're pregnant.
Are chickenpox parties a good idea?
Research has shown that one in eight parents said they would consider deliberately exposing their child to chickenpox in order to get the illness 'out of the way'.
Most experts agree this is not a good idea, including nurse Sharon White:
'As a busy working mum myself, who had four children under five, I can completely understand why parents would consider the potential benefit of exposing children to chickenpox via 'parties' so that they all get it at one time.
'However, this is not something I would advocate.
'Children and babies have individual immune systems and, therefore, individual abilities to react and recover from infectious diseases.
'Although chickenpox is often mild in young children we sometimes see more serious cases and I feel it would be irresponsible to deliberately expose a child to potential risk.
'Imagine how you would feel if your child was the one in 1,000 who was admitted to hospital with complications and you had deliberately exposed them.'
It is widely believed that parents should allow their child to experience the illness naturally.
What's the best way to stop chickenpox itching?
You probably remember being covered from head to toe in calamine lotion, but these days experts, including Sharon, believe that there are better products available that cool or reduce itching, without drying out the skin.
- Virasoothe Pharmacists often recommend using a product called Virasoothe chickenpox relief cooling gel. It is clinically proven to support natural healing and reduce scarring and is safe to use on babies and children over the age of six months.
- Antihistamine Speak to your pharmacist about using an antihistamine to help reduce the itching
Other tips include:
- Loose-fitting, smooth, cotton clothing It helps stop the skin from becoming sore and irritated
- Put on cotton socks or scratch mitts on at night This helps prevent them scratching off scabs or breaking the skin. Also keep fingernails clean and short.
- Put porridge oats in bath water Simply fill a clean sock with porridge oats, knot it, and let the tap run through it so the water turns milky. It's thought to help ease itching. Don't use any other products in the bath.
- Ice lollies It's important to keep children hydrated. If they've got spots in their mouths, ice lollies can help ease the discomfort.
Why is it dangerous to give ibuprofen during chickenpox?
If your child is suffering from chickenpox, you should not give him ibuprofen.
Professor Nigel Mathers of the Royal College of GPs, says:
'Parents with sick children need to be certain that any medication they give them will not have any adverse reaction or cause them more distress. Given the current uncertainty around the use of ibuprofen on chickenpox, it would be wise for parents to stick to paracetamol.
Ibuprofen can be used again safely once the child is clear of chickenpox and the spots have disappeared.'
The NHS advises that 'paracetamol is the preferred painkiller for treating the associated symptoms of chickenpox'.
It is also very important that children are not given aspirin either as it can be dangerous for anyone under the age of 16.
Can you be immune to chickenpox, without ever having it?
Latest research shows that 90% of children will get chickenpox before the age of 10, with a large number of cases before they reach the age of five.
However, some children do seem to resist catching it when it does the rounds at nursery or school. Whether that means they are immune to it or not, can only be detected with a blood test.
Remember that some cases of chickenpox are so mild that it could be possible for a parent or child not to notice it. Just noticing one spot could be enough to mean you've had it and are now immune to the disease.
I've heard chickenpox spots can get infected. How will I know if this happens?
'Very occasionally, the blisters can become infected and the most obvious sign is when the surrounding skin becomes red and sore,' says nurse Sharon White.
If you think that your child's blisters have become infected, contact your GP as he may need a course of antibiotics.
He may also benefit from some pain relief and your local pharmacist will be able to recommend what is the most suitable for him.
What's the incubation period of chickenpox?
If someone your child has been playing with gets chickenpox then you'll probably be waiting for the spots to appear on your child (if he hasn't had it yet) any day.
You could be waiting a while for chickenpox spots to show, though. The NHS guidelines suggest that symptoms of chickenpox start one to three weeks after becoming infected, so your child's spots may not appear for weeks.
The NHS also states that 'someone with chickenpox is infectious from one or two days before the rash appears until all the blisters have dried out and crusted over.'
If someone in your household has chickenpox then it's worth knowing that there is a 90% chance of spreading it to another family member.
Of course, it often feels as though your other children are most likely to get it just as the first one is recovering, just so that you can enjoy another week of scratch-patrol!
Can you catch shingles from chickenpox?
Chickenpox and shingles are both caused by the same virus: the varicella-zoster virus (VZV).
Once you've had chickenpox, the virus stays in your system causing no harm. However, it can be reactivated later in life and cause shingles – something that doctors believe happens with age, stress or a lowered immune system.
You can't catch shingles from chickenpox – nor can you catch shingles from someone with shingles.
However, you can catch chickenpox from someone with shingles, if you haven't had chickenpox before.
Can I still breastfeed if I have chickenpox?
Chickenpox can't be passed on through breastmilk.
According to NCT, 'if a woman is already immune she cannot give chickenpox to her baby. If a woman isn’t immune and she gets chickenpox, her baby will be likely to catch chickenpox from her.
'If she is breastfeeding, her baby will receive help in fighting the infection through the antibodies in her milk (the infection cannot be passed on through breastmilk).'
The latest advice from the National Breastfeeding Helpline is this:
'Mothers who contract chickenpox can breastfeed as normal. Any vesicles [fluid filled spots] on the breast should be covered to minimise the risk of transmission from virus within vesicles.'
For any worries about breastfeeding through illness, contact the National Breastfeeding Helpline.
Related stories
Things to do when you're stuck indoors with chickenpox
CHAT: What's a good age for a child to catch chickenpox
Sources
- NHS. 2017. Chickenpox
- Patient. 2018. Chickenpox in children
- NICE. 2018. Chickenpox - Clinical Knowledge Summary






